Plating on Plastics: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing Durability and Aesthetics
Introduction to Plating on Plastics
Plating on plastics is an advanced surface treatment technique that involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto a plastic substrate. This process combines the benefits of both metal and plastic materials, providing enhanced durability, conductivity, and aesthetic appeal.
Benefits of Plating on Plastics
Enhanced Durability and Wear Resistance
Plating plastics improves the overall durability and wear resistance of the plastic component. The deposited metal layer provides additional strength and protection against mechanical stress, abrasion, and environmental factors.
Improved Electrical Conductivity
Plating on plastics can also enhance electrical conductivity, making it an excellent choice for electronic components and connectors. The metal layer helps reduce electrical resistance, thereby improving the overall performance of the part.
Aesthetic Appeal
Plating on plastics imparts the substrate a high-quality, metallic finish, increasing its visual appeal. This is particularly advantageous in industries where appearance is crucial, such as automotive, consumer electronics, and jewelry.
Selecting the Right Plastic Material
The success of the electroplating process largely depends on the selection of the appropriate plastic material. The following factors must be considered when choosing the right plastic substrate:
Chemical Resistance
The plastic must be resistant to the chemicals used in the electroplating process. Some suitable plastics with good chemical resistance include ABS, PBT, and PC.
Thermal Stability
The plastic material must withstand the high temperatures involved in the electroplating process. Materials such as PEEK, PPS, and LCP exhibit excellent thermal stability, making them ideal candidates for electroplating.
Adhesion Compatibility
The plastic substrate should have a surface that promotes adhesion between the metal and the plastic. ABS and PC/ABS blends are known for their excellent adhesion properties, which makes them popular choices for electroplating.
Pre-treatment Processes for Plastics
Proper pre-treatment of the plastic substrate is essential for a successful electroplating process. The pre-treatment steps include:
Cleaning
The surface of the plastic must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants, such as dust, grease, or mold-release agents. This can be achieved using ultrasonic cleaning, solvent cleaning, or a combination of both.
Etching
Etching is performed to create a roughened surface on the plastic, which promotes better adhesion between the metal layer and the plastic substrate. Common etching techniques include chemical etching using chromic acid or a permanganate-based solution.
Activation
Activation is the process of applying a catalyst to the plastic surface, making it receptive to the electroless plating process. Palladium chloride is a common catalyst used for this purpose. We also use a copper conductive paint before the plating begins.
Electroless Plating and Electroplating on Plastics
Two primary methods for depositing metal layers onto plastic substrates are electroless plating and electroplating.
Electroless Plating
Electroless plating is an autocatalytic process that deposits metal onto the plastic surface without using an external electrical current. The process relies on a chemical reaction between the plastic substrate and the plating solution, which contains metal ions, reducing agents, and stabilizers. Electroless plating offers uniform metal deposition, even on complex geometries.
Advantages of Electroless Plating:
- Uniform metal deposition
- Excellent adhesion
- No need for external electrical current
- Ability to plate complex geometries
Electroplating
Electroplating is an electrolytic process that uses an electrical current to reduce metal ions from a plating solution onto the surface of the plastic substrate. This method typically follows electroless plating to enhance the properties of the plated component further. Here at Elite Luxury we use the electroplating method.
Advantages of Electroplating
- Precise control over metal deposition thickness
- Wide range of metal plating options
- High-quality, shiny finish
- Enhanced durability and wear resistance
Common Metals Used for Plating on Plastics
Various metals can be used for plating plastics, each offering unique benefits and applications. Some of the most common metals include:
- Nickel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and a lustrous finish
- Copper: Enhances electrical conductivity and offers a cost-effective solution is also a good base metal for the first layer
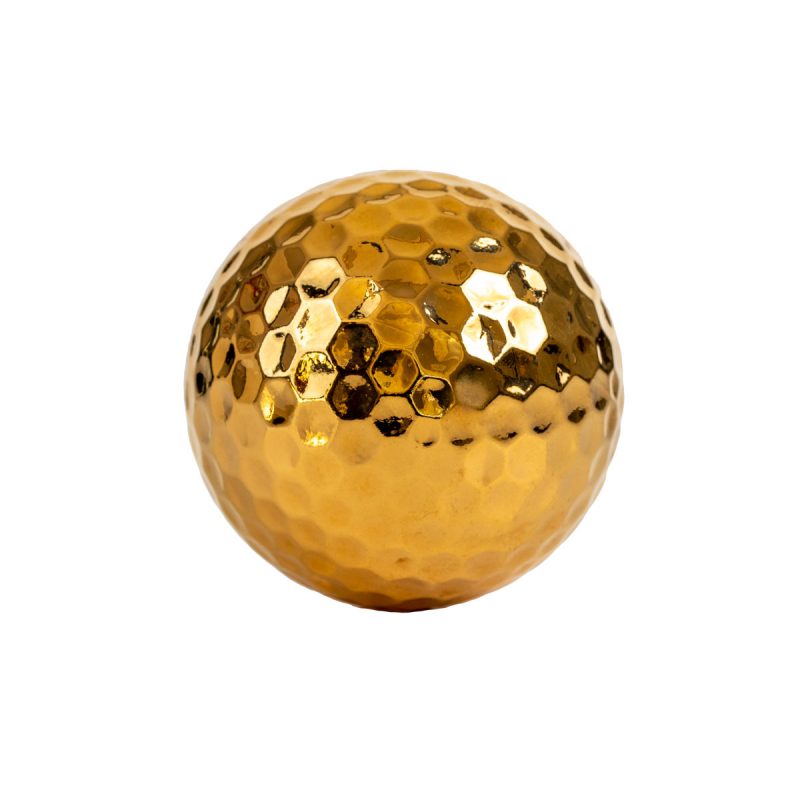
- Gold: Offers superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and a luxurious aesthetic appeal
- Silver: Features excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, along with a shiny finish
- Chrome: Imparts a bright, mirror-like finish and excellent wear resistance
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure the quality and performance of electroplated plastic components, rigorous testing and quality control measures should be implemented. Some of the most common tests include:
Adhesion Testing
Adhesion testing is crucial for assessing the bond strength between the metal layer and the plastic substrate. Common adhesion tests include tape tests, bend tests, and peel tests.
Thickness Measurement
The thickness of the metal layer can be measured using non-destructive methods, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or magnetic induction, to ensure the plated components meet specifications.
Surface Inspection
Visual inspection and microscopic examination can be used to identify surface defects, such as pits, scratches, or uneven plating.
Functional Testing
Depending on the intended application of the electroplated component, functional tests, such as electrical conductivity or wear resistance tests, may be necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Applications of Electroplated Plastics
Electroplated plastics have found widespread use in various industries due to their unique combination of properties. Some of the most common applications include:
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry extensively uses electroplated plastic components for interior and exterior applications. Examples include:
- Emblems and logos
- Grilles
- Door handles
- Mirror housings
- Interior trim pieces
Consumer Electronics
Electroplated plastic components play a significant role in the consumer electronics industry, offering functional and aesthetic benefits. Examples include:
- Mobile phone casings
- Laptop housings
- Connector shells
- Electronic switches and buttons
Medical Devices
The medical device industry also benefits from electroplated plastics, as these components provide enhanced durability, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Also, with gold being hypoallergenic, gold plating can be used on items such as hearing aids. Other Examples include:
- Surgical instrument handles
- Dental tools
- Diagnostic equipment housings
Aerospace and Defence
In the aerospace and defence sectors, electroplated plastics offer lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant components. Examples include:
- Avionic housings
- Control panel components
- Connector shells
Jewelry and Accessories
Electroplated plastic components can also be found in the jewelry and accessory industries, providing a cost-effective and lightweight alternative to traditional metal components. Examples include:
- Watch casings
- Fashion jewelry
- Belt buckles
- 3D prints
By understanding the specific requirements of each industry and application, manufacturers can optimize the electroplating process to create high-quality, reliable, and visually appealing components that meet the needs of their customers.
Environmental Considerations in Plating on Plastics
Environmental sustainability is an essential aspect to consider when performing electroplating on plastics. Manufacturers must take appropriate measures to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulatory standards. Key considerations include:
Responsible Chemical Management
Proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals used in electroplating are crucial for protecting the environment and maintaining a safe workplace. Implementing a chemical management system can help ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives can significantly minimize the environmental footprint of the electroplating process. These initiatives may include:
- Recycling process water
- Recovering and reusing metal ions from rinse water
- Implementing a closed-loop system for chemicals and waste
Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient equipment and technologies can help reduce the overall energy consumption of the electroplating process. Examples of energy-saving measures include:
- Using high-efficiency power supplies
- Implementing energy management systems
- Optimizing process parameters to minimise energy consumption
By proactively addressing environmental concerns, manufacturers can reduce their environmental impact and enhance their reputation and competitiveness in the market.
Final Thoughts
Electroplating on plastics is a powerful and versatile technique for enhancing the properties and appearance of plastic components. With a thorough understanding of material selection, pre-treatment processes, plating methods, quality control, and environmental considerations, manufacturers can produce high-quality electroplated plastics that meet the demanding requirements of various industries. As technology advances, we can expect electroplated plastics to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Plating On Plastics By Elite Luxury Gold Plating
At Elite Luxury Gold Plating, we specialise in plating on plastic services using the electroplating technique. Our process begins with electroplating copper onto the substrate and adding finishes. Apart from plastic, we cater to a variety of materials, including:
- ABS and other plastics
- Resin
- Sea shells (require additional pre-processing)
- Ceramic
- Glass
- Bamboo
- Bone
- Golf Balls
- 3D prints
For a quote on plating your non-metal item, please click here to get in touch with us.